Canonical MicroK8s
 |
MicroK8s is the simplest production-grade conformant K8s. Lightweight and focused. Single command install on Linux, Windows and macOS.
Prerequisites
The L7|ESP Helm chart can be installed onto a multi-node MicroK8s cluster running on traditional VMs:
A fleet of virtual machines (e.g. Ubuntu) to convert into MicroK8s nodes
Requirements (Amazon EC2)
To install the L7|ESP Helm chart on Amazon EC2 Instance, you must have:
An AWS account to deploy to
Access keys for the AWS account (see Managing access keys for IAM users)
aws command line tool will be use to programmatically access the AWS account. To install the AWS CLI tool, follow the link below and choose the correct operating sytem:
Infrastructure as Code
CloudFormation Template
The latest CloudFormation template is as follows:
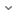 CloudFormation template
CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Parameters:
InstanceTypeParameter:
Type: String
Default: t3a.medium
Description: Enter instance size. Default is t3a.medium.
SSHLocation:
Description: The IP address range that can be used to SSH to the EC2 instances
Type: String
MinLength: '9'
MaxLength: '18'
Default: 0.0.0.0/0
AllowedPattern: '(\d{1,3})\.(\d{1,3})\.(\d{1,3})\.(\d{1,3})/(\d{1,2})'
ConstraintDescription: Must be a valid IP CIDR range of the form x.x.x.x/x
AMI:
Type: String
Default: ami-08c40ec9ead489470
Description: The Linux AMI to use.
Key:
Default: l7esp-ec2-linux
Description : Name of an existing EC2 KeyPair to enable SSH access to the instance
Type: String
VPC:
Type: String
Default: vpc-0278eb63cfc078a74
Description: The key used to access the instance.
Resources:
InstanceSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupName: "Internet Group"
GroupDescription: "SSH and web traffic in, all traffic out."
VpcId: !Ref VPC
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: '22'
ToPort: '22'
CidrIp: !Ref SSHLocation
SecurityGroupEgress:
- IpProtocol: -1
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
Linux:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::Instance'
Properties:
ImageId: !Ref AMI
InstanceType:
Ref: InstanceTypeParameter
KeyName: !Ref Key
SecurityGroupIds:
- Ref: InstanceSecurityGroup
BlockDeviceMappings:
- DeviceName: /dev/sda1
Ebs:
VolumeSize: 100
Tags:
-
Key: Appplication
Value: Linux Server
-
Key: Domain
Value: None
-
Key: Environment
Value: Test
-
Key: LifeTime
Value: Transient
-
Key: Name
Value: l7esp-ec2-linux-MicroK8s
-
Key: OS
Value: Linux
-
Key: Purpose
Value: Support Test Instance
Outputs:
PublicIp:
Value:
Fn::GetAtt:
- Linux
- PublicIp
Description: Server's PublicIp AddressParameters
InstanceTypeParameter(String) - The desired name of your AWS EKS Cluster.SSHLocation(String) - The IP address range that can be used to SSH to the EC2 instances. (Default: 0.0.0.0/0)AMI(String) - The desired AMI ID (Here are few suggested AMI’s AMI Amazon Linux (Recommended), Debian Stable, Ubuntu LTS releases)Key(String) - This for Tag with Keyan Name as required for your AWS EC2 InstanceVPC(String) - This is a VPC ID where you want to provision EC2 Instance
Parameters File
Create a parameters.json file for use when deploying the CloudFormation template:
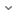 CloudFormation template
CloudFormation template
[
{
"ParameterKey": "InstanceTypeParameter",
"ParameterValue": "c6g.4xlarge"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "SSHLocation",
"ParameterValue": "0.0.0.0/0"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "AMI",
"ParameterValue": "ami-0f69dd1d0d03ad669"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "Key",
"ParameterValue": "l7esp-ec2-linux"
},
{
"ParameterKey": "VPC",
"ParameterValue": "vpc-0278eb63cfc078a74"
}
]Provisioning
Create a profile for use with AWS CLI:
~$ aws configure --profile <profile> AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE AWS Secret Access Key [None]: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY Default region name [us-east-1]: Default output format [None]:
Switch to the correct AWS profile for current shell session:
~$ export AWS_PROFILE=<profile>
Deploy CloudFormation stack:
$ aws cloudformation deploy \ --stack-name l7esp-ec2 \ --template-file amazon_linux_ec2.yml \ --parameter-overrides file://ec2.parameters.json \ --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
Validate Resource Creation
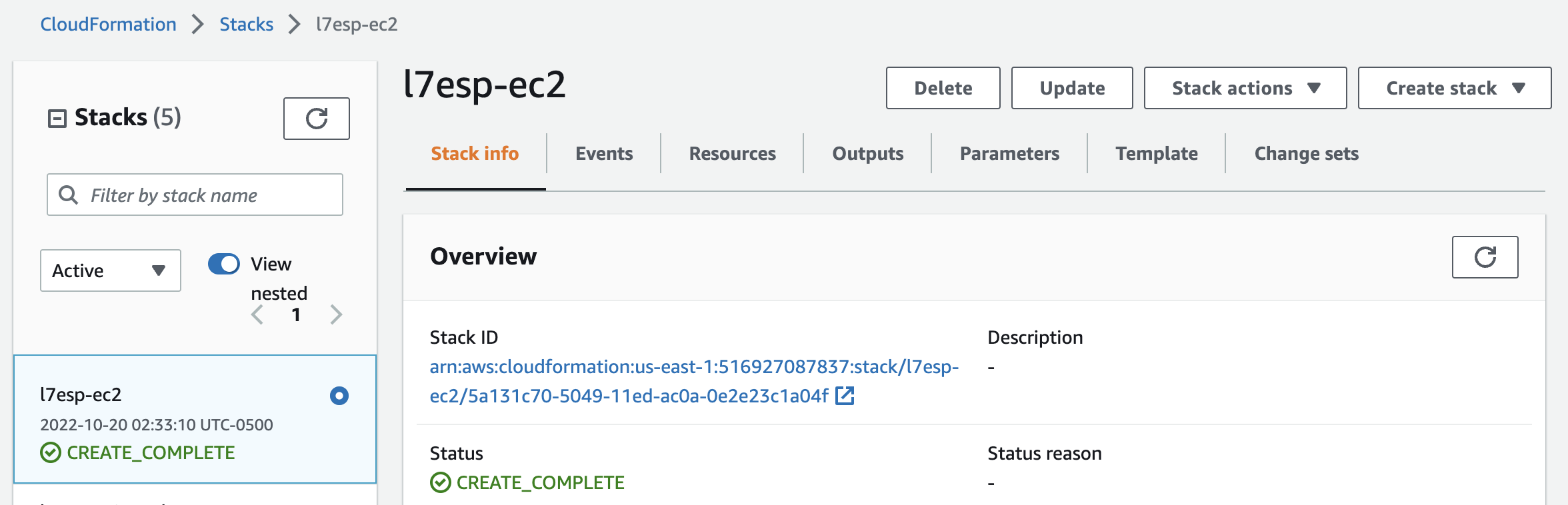
Log into the AWS Console and navigate to CloudFormation. Under “Stacks”, validate that the CloudFormation stack was created:
Install MicroK8s
The installation steps for Ubuntu are, roughly, as follows:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get upgrade -y $ sudo snap install core $ sudo snap install microk8s --classic --channel=1.25/stable $ microk8s enable dns $ microk8s enable hostpath-storage $ sudo microk8s status --wait-ready $ sudo usermod -a -G microk8s l7esp $ sudo chown -f -R l7esp ~/.kube $ echo -e "l7esp\nl7esp" | passwd root $ echo "alias kubectl='microk8s kubectl'" >> ~/.bash_rc
Note
Please refer to the official documentation for latest advice on how to install MicroK8s. The steps above are merely for demonstation purposes. Install a local Kubernetes with MicroK8s
Access the Kubernetes cluster
SSH into one of the cluster’s master node and check that all nodes were provisioned and are in Ready state, with the following command:
$ microk8s kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master Ready <none> 1h v1.20.13-35+d877e7a8ac536e k8s-node-1 Ready <none> 1h v1.20.13-35+d877e7a8ac536e k8s-node-2 Ready <none> 1h v1.20.13-35+d877e7a8ac536e
Installing L7|ESP Helm chart
To install L7|ESP on the new Kubernetes cluster, see the Helm deployment guide.
Note
MicroK8s comes with its own packaged version of the Kubernetes CLI so remember to use the microk8s kubectl to ensure you are using the correct version when controlling the cluster.