Reference: Creating Custom Queries
This document is intended to provide information to developers interested in developing custom database queries
General Information
Custom queries can be contributed as YAML files under the project ./content/queries folder
A name and query property must be specified\
The parameters property is also often used to allow the query to return dynamic results based on arguments
Custom queries will be registered under an endpoint of the format /api/v2/queries/filename_of_custom_query
The queries can also be executed from the backend with the lab7.main.api.run_named_query function
Example custom query .yaml file:
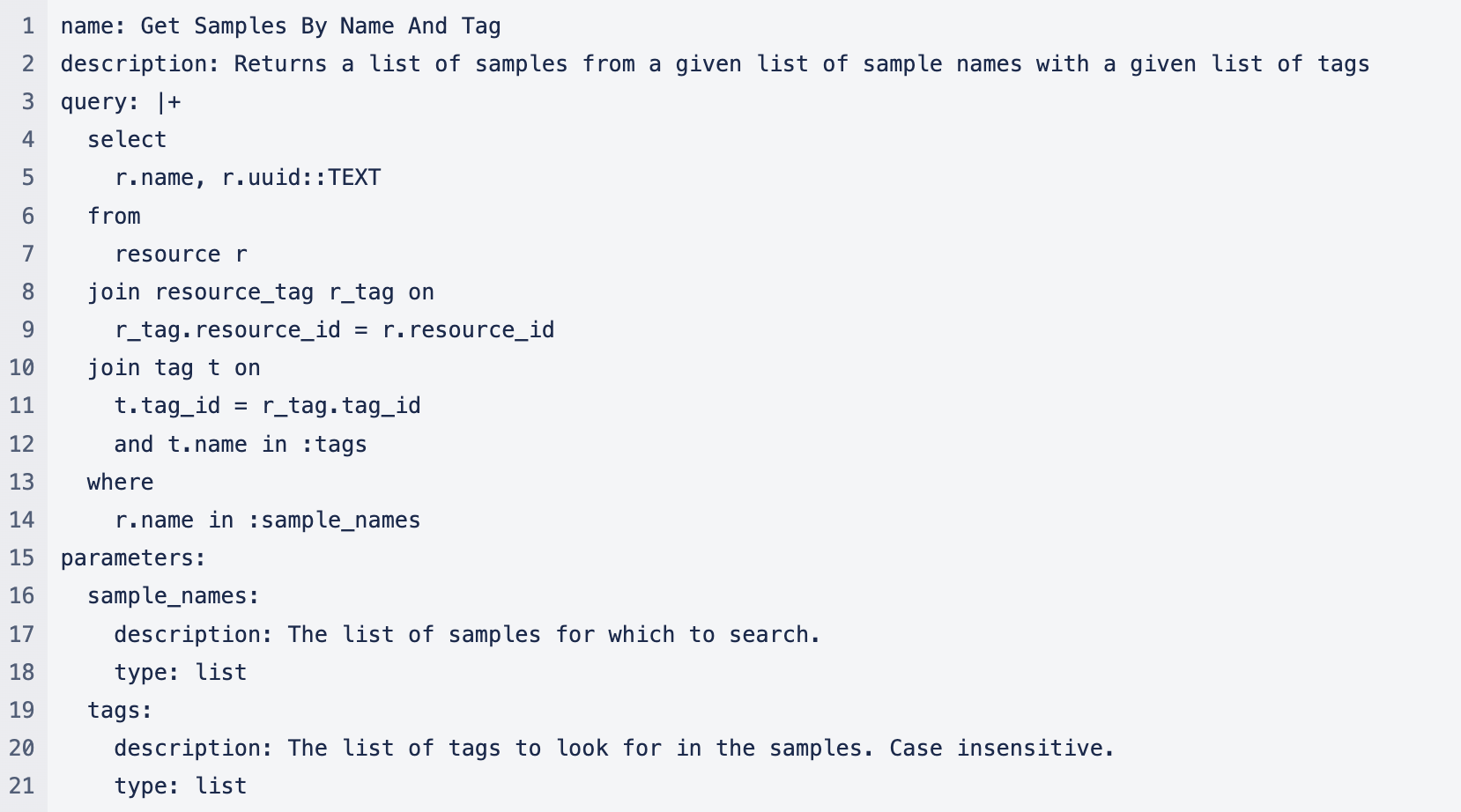
Commonly Used Tables for Implementations
resource
Common joins: resource_val (via resource_val.bound_resource_id ↔︎ resource.resource_id FK relationship)
workflowable_resource (samples, containers, and item rows stored here)
resource_var
Common joins: resource (via resource_var.resource_var_id ↔︎ resource.resource_id FK relationship)
resource_val
Common joins: resource_var (via resource_val.resource_var_id ↔︎ resource_var.resource_var_id FK relationship)
step_instance_sample
Common joins: resource_val (via step_instance_sample.association_id ↔︎ resource_val.step_instance_sample_id FK relationship)
resource_dependency
Primary use-case for recursive queries
resource_action
Audit log
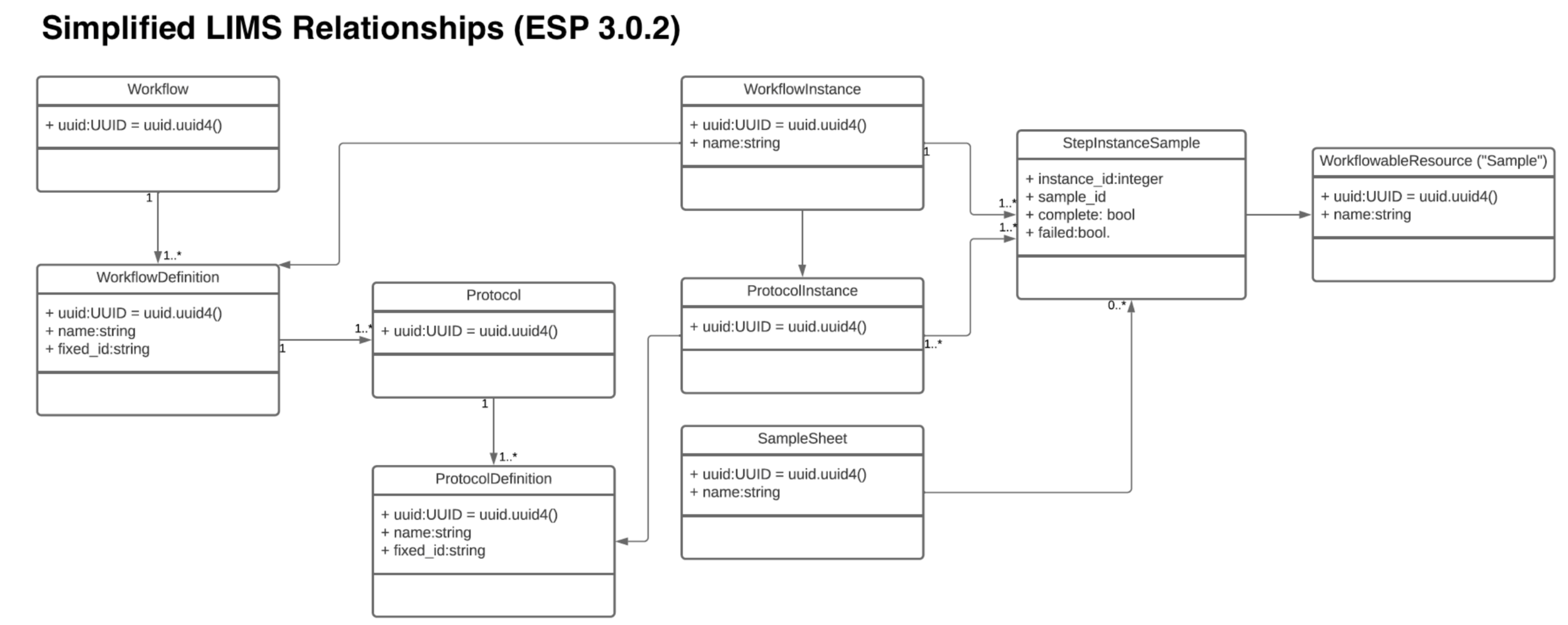
Simplified LIMS Relationship (3.0.2)
The image below displays important Foreign Key relationships - most models derive from the more abstract Resource table
The resource table stores some of the more important properties such as resource name, url, uuid, created_timestamp, barcode
For resource values (LIMS, custom entity fields), the fixed_id is the resource.barcode which may be a more stable lookup than resource.name (display name)
Often, users will check here for the matching resource name, then joining back tables for the report
Example Query for Pulling LIMS Process Data
To constrain the results, developers should add a WHERE clause to the statement
Users may be much more targeted by restricting to a specific workflowable resource type, or a resource variable name/barcode (display name / fixed_id)
It may also be beneficial to consider starting from the sample type, the sample sheet, the experiment
As the database size grows, it would be helpful to paginate and add filters to the results to limit the number of rows returned

Example of Function to be Used in an Invokable(backend function), Query is Built Without Using SQL Alchemy Models
Consider using the standard REST APIs if they meet the organization’s needs and are performant enough for the use case
They support LIMIT & OFFSET for pagination, and additional params to hydrate additional aspects on the underlying SQL Alchemy ORM models may be requested
Consider both the /api/resources endpoint and the /api/samples endpoint (resource filters also applicable to most models)

Resources
The term "resource" refers to any ESP object that has an associated uuid
Most resources have associated attributes, such as names, descriptions, and tasks
ESP objects classified as a resource (see esp_cls_definition table for full listing):
File
User
Role
Lab
Task
Pipeline
Task Instance
Pipeline Instance
Task Definition
Pipeline Definition
Report
Step
Protocol
Workflow
Component
Step Definition
Protocol Definition
Workflow Definition
Step Instance
Protocol Instance
Workflow Instance
Sample Sheet
Sample
Sample Type
Sample Type Definition
Project
Container
Container Type
Container Type Definition
Param Group