Pipelines: ESP Client and Debugging Tips
ESP Client
The ESP Client is a Python package with two interfaces:
A command-line interface for importing and exporting content (which you should already be familiar with)
A collection of Python modules that can be used in other Python scripts or packages
The Python modules provide an Object Relational Mapper for interacting with ESP objects as if they are Python objects, without having to explicitly make any REST API calls. These ESP objects include almost everything you see in the ESP UI, such as Samples, Entities, Containers, Workflows, Worksheets, Items, etc. Anything you can do in the UI, you can also do programmatically using the ESP Client.
Take some time to review the ESP Client documentation. In the documentation you’ll find a collection of Python classes that correspond to different data models in ESP.
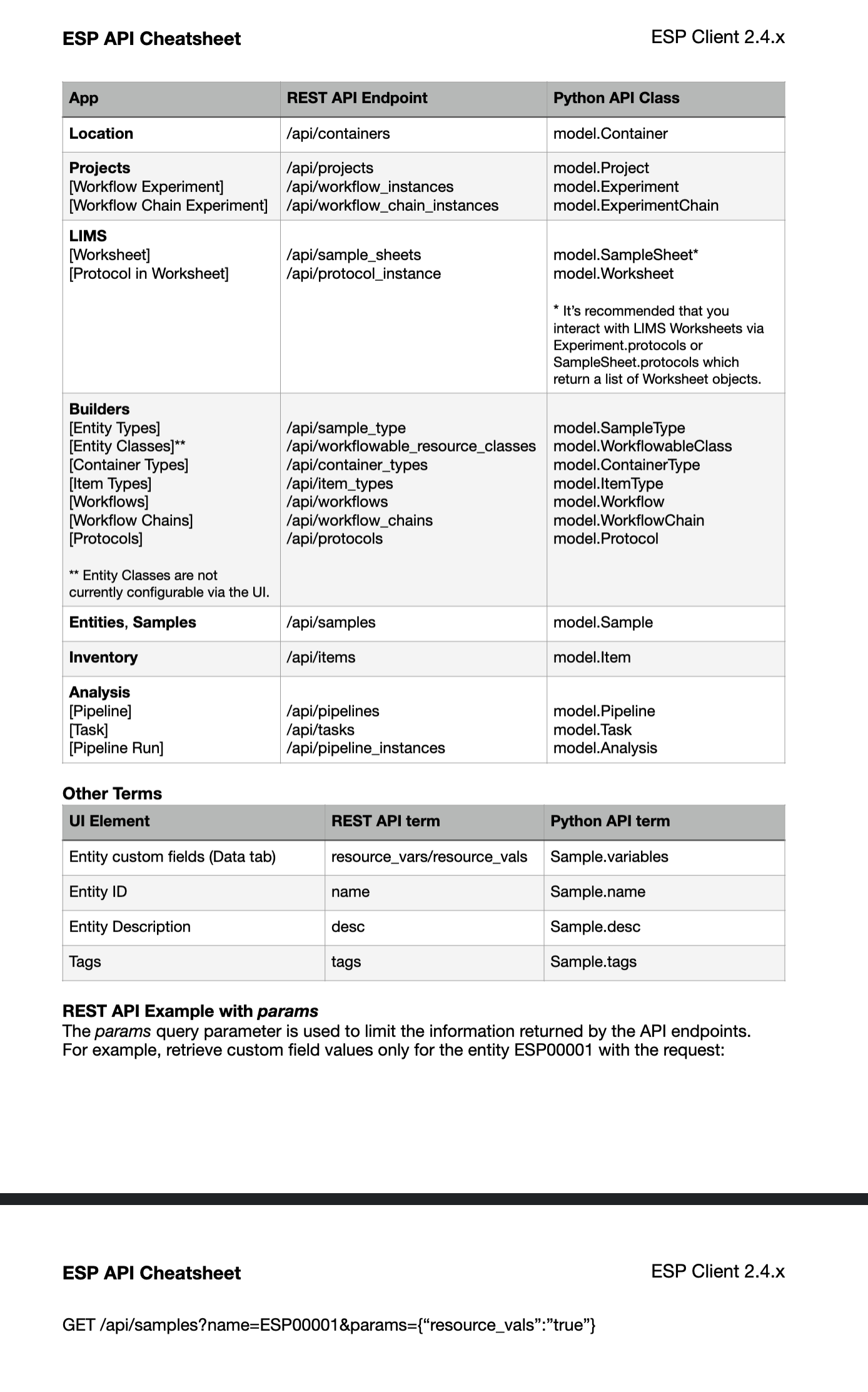
We have also provided an ESP Client cheatsheet which will help you to conceptually map parts of the ESP UI to the different APIs.
Debugging and Development Tips
For developing and debugging Pipeline scripts, there are a few approaches:
Prototype or debug snippets of code in a standard python terminal
Modify your pipeline script so that it can be run manually in the client python environment with a debugger
Write to
stderrusingsys.stderr.write(be careful usingprintstatements because Python will not automatically flush the contents ofstdoutif the script errors out and you might miss important information)
If you would like to use an ipython terminal, first install the ipython package into the client environment:
(base) l7esp@d60b8b032978:~/data/project$ pip install ipython
To launch an ipython shell, run the following in the terminal:
(base) l7esp@d60b8b032978:~/data/project$ ipython
If running import esp within the ipython terminal still gives an error, you might have to reactivate the client environment to get the paths to register correctly:
source ~/data/extensions/client/bin/activate
Best Practices for Developing Pipeline Scripts
In general, the best practices for developing pipeline scripts are the same best practices for developing any software. However, there are a few performance considerations to be aware of when using the ESP Client APIs:
Avoid constructing or updating client objects inside of a loop. Each time an object is created, the client makes a REST API call over the network. If your script makes hundreds of these calls in a loop, you could overwhelm the back-end and have your script timeout.
Similarly look for evidence of N+1 queries.
For complex runsheet generation, utilize the Generic Runsheet Generation patten described above
When updating a protocol in a worksheet, set
evaluate=Falsewhen callingprotocol.save()unless you need expressions to be re-evaluated in the protocol.