Modeling Entity Classes and Entity Types
In this section
This section will help you:
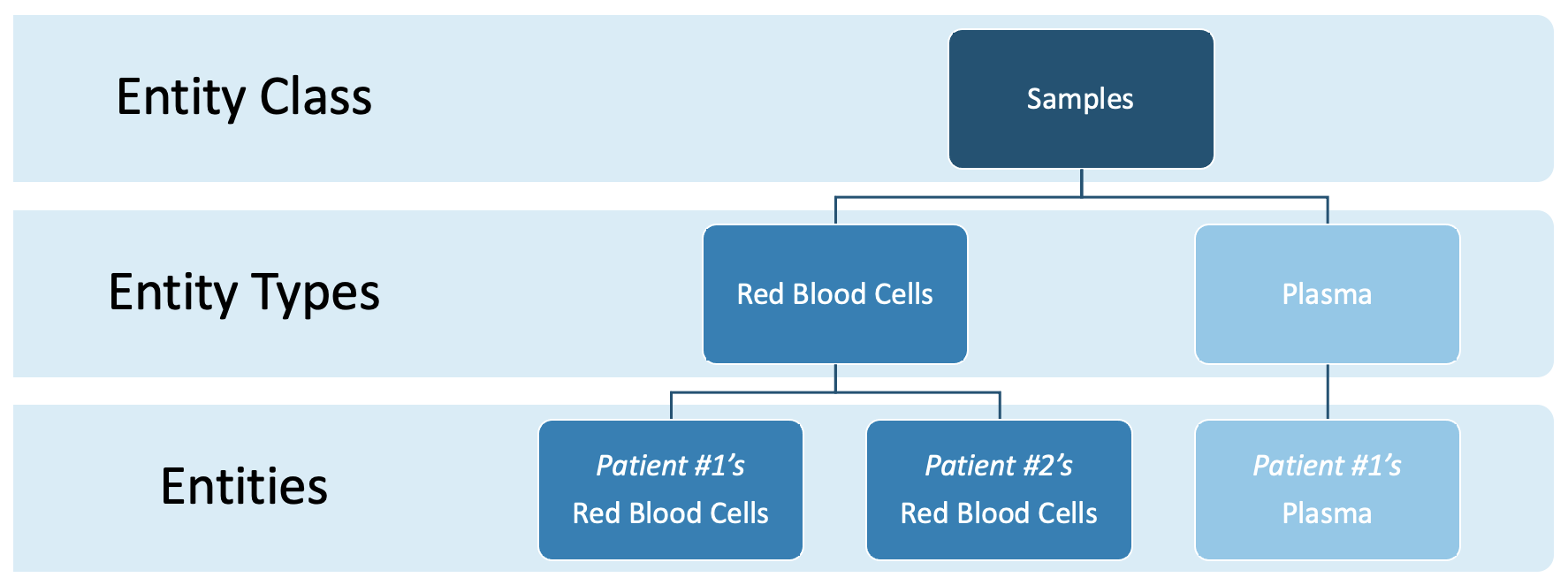
Understand the relationship between Entity Class, Entity Type, and Entity.
Understand design considerations and best practices for modeling Entities.
Know how to create new Entity Classes and Entity Types.
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Entity | A resource that is submitted to or a component of a business process. Entities are instances, or occurrences, of Entity Types. |
Entity Type | Defines the attributes of an Entity, including its custom fields and ID Sequence(s). |
Entity Class | A categorical way of grouping different Entity Types. Each Entity Class will receive its own app in L7|ESP, useful for managing User access. |
Instance | In object-oriented programming, an instance is a specific realization of any object. |
Custom Fields | Entity data defined at the level of the Entity Type. |
Var Groups | Organize custom fields into tabs on the Entity details page. |
Workgroups | Used to organize Users and restrict access to content. |
When an End User views an Entity, they see:
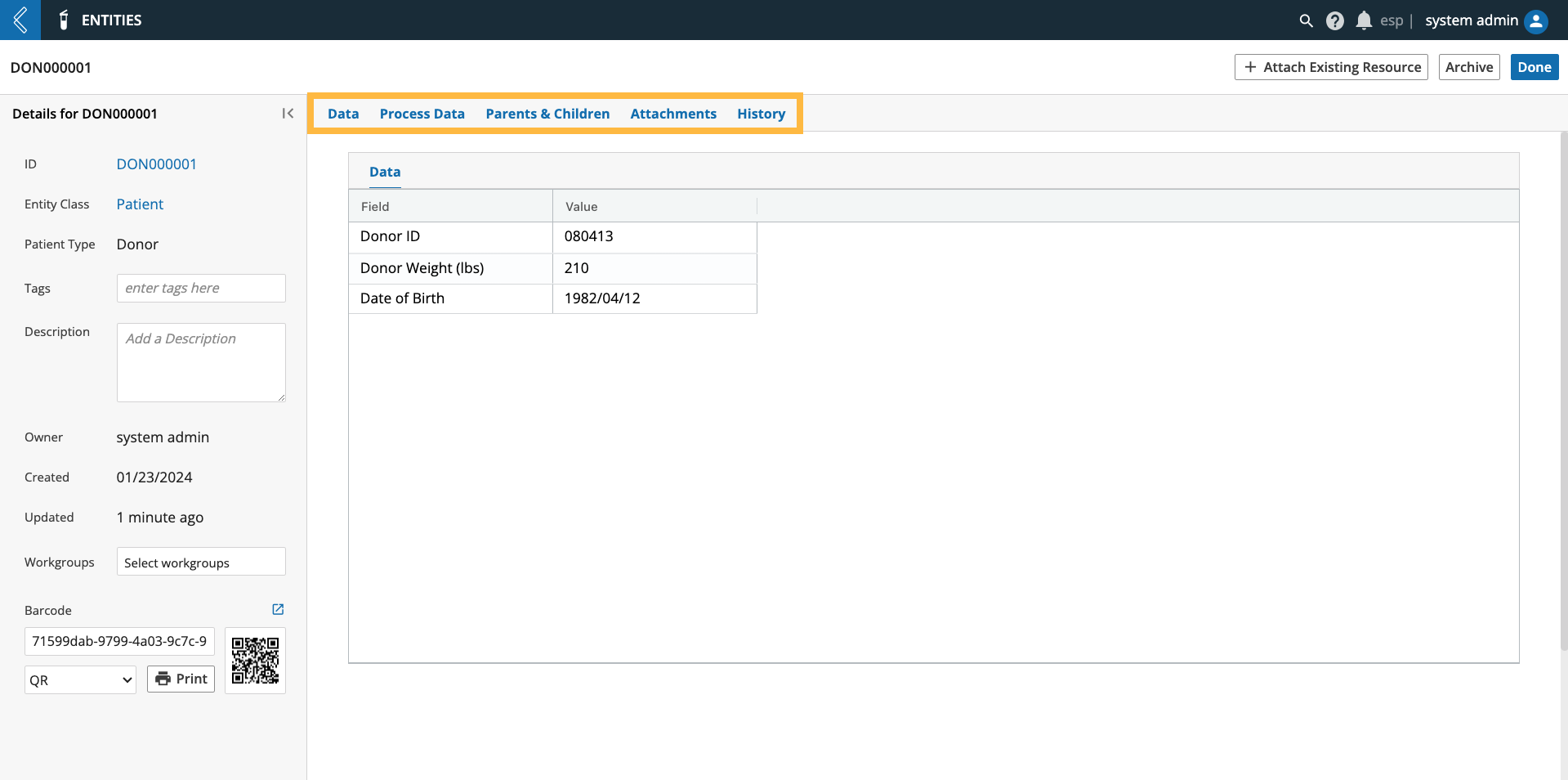 |
The Entity’s metadata (Data tab).
Experimental data associated with the Entity (Process Data tab).
The Entity’s relationship to other Entities (Parents & Children tab).
The files the Entity is associated with (Attachments tab).
The Entity’s history (History tab).
Entities are at the center of all processes modeled in L7|ESP, which is why we begin by modeling these resources. It is also the reason L7|ESP is agnostic to any business process in the life sciences and healthcare.
When to create an Entity Class?
If more than one (1) Entity Type can be organized into the same category.
If you want to restrict access to a category of Entities.
When to create an Entity Type?
If you have a resource that you wish to register and track as part of a business process.
Containers and Items have their own data models in L7|ESP.
If two (2) Entities have different custom fields.
More than one (1) ID Sequence can be assigned to the same Entity Type, assuming these different Entities share the same custom fields.
Design Considerations:
When in the process will this Entity Type be created?
Is there any data that needs to be attributed to this Entity Type?
How will this data be collected?
What Sequence IDs need to be attributed to this Entity Type?
Do these IDs require any contextual data?
What contextual data is available for Sequence IDs?
Are there legacy Entities that need to be migrated into L7|ESP?
Does this Entity Type require a custom view?
Should this custom view be applied to all Entity Types in the assigned Class?
Note
Custom Entity views are covered in more detail here and in the Developer MasterClass.
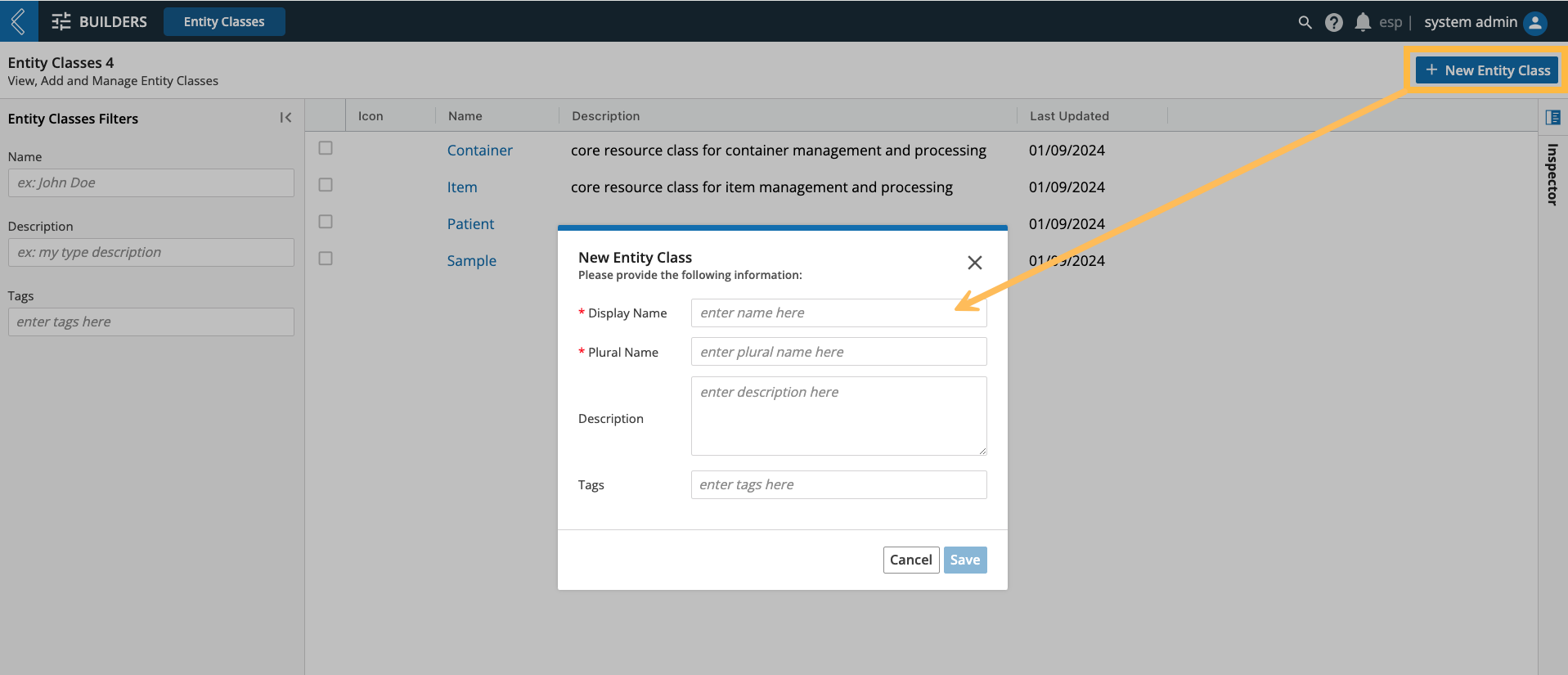
Go to: Builders (L7|Master) → Entity Classes → + New Entity Class
 |
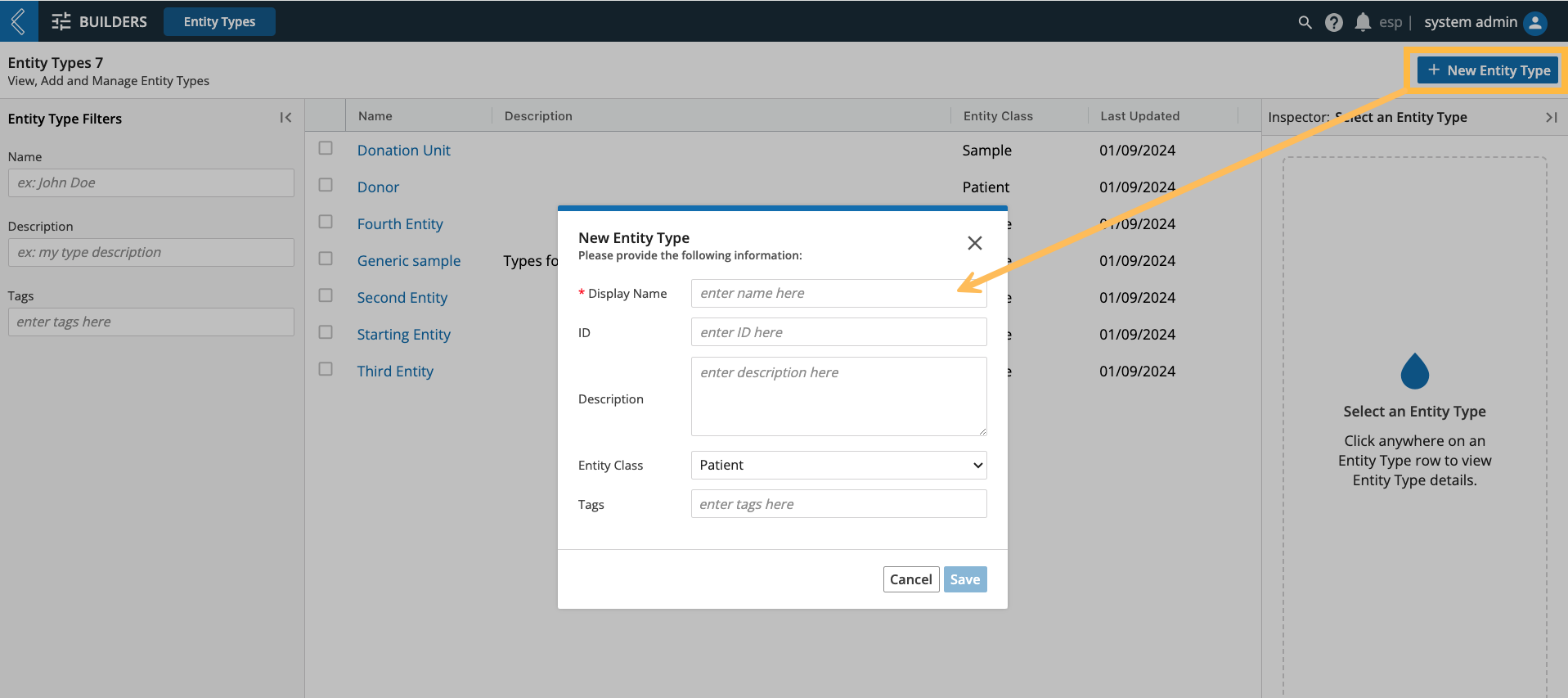
Go to: Builders (L7|Master) → Entity Types → + New Entity Type
Display Name and Entity Class are required fields.
Note that the Entity Class must be created first in order to appear as an option.
Note
Display Name vs. ID: Display Name is the name that appears in the user interface (UI). ID is a fixed value used to reference the resource. This differentiation ensures stability when changing the name of a resource (i.e., Entity).
L7|ESP will set the Display Name as the ID if the User does not define the ID themselves.
Entity Class: L7|ESP has three (3) core classes: Sample, Container, and Item. Containers in the Location app and Items in the Inventory app automatically belong to class Container and Item, respectively.
Newly created Entity Types cannot be assigned to these two (2) classes.
 |
Custom fields define the immutable properties of an Entity Type.
Go to: Builders (L7|Master) → Entity Types → select the Entity Type → + Add Custom Field
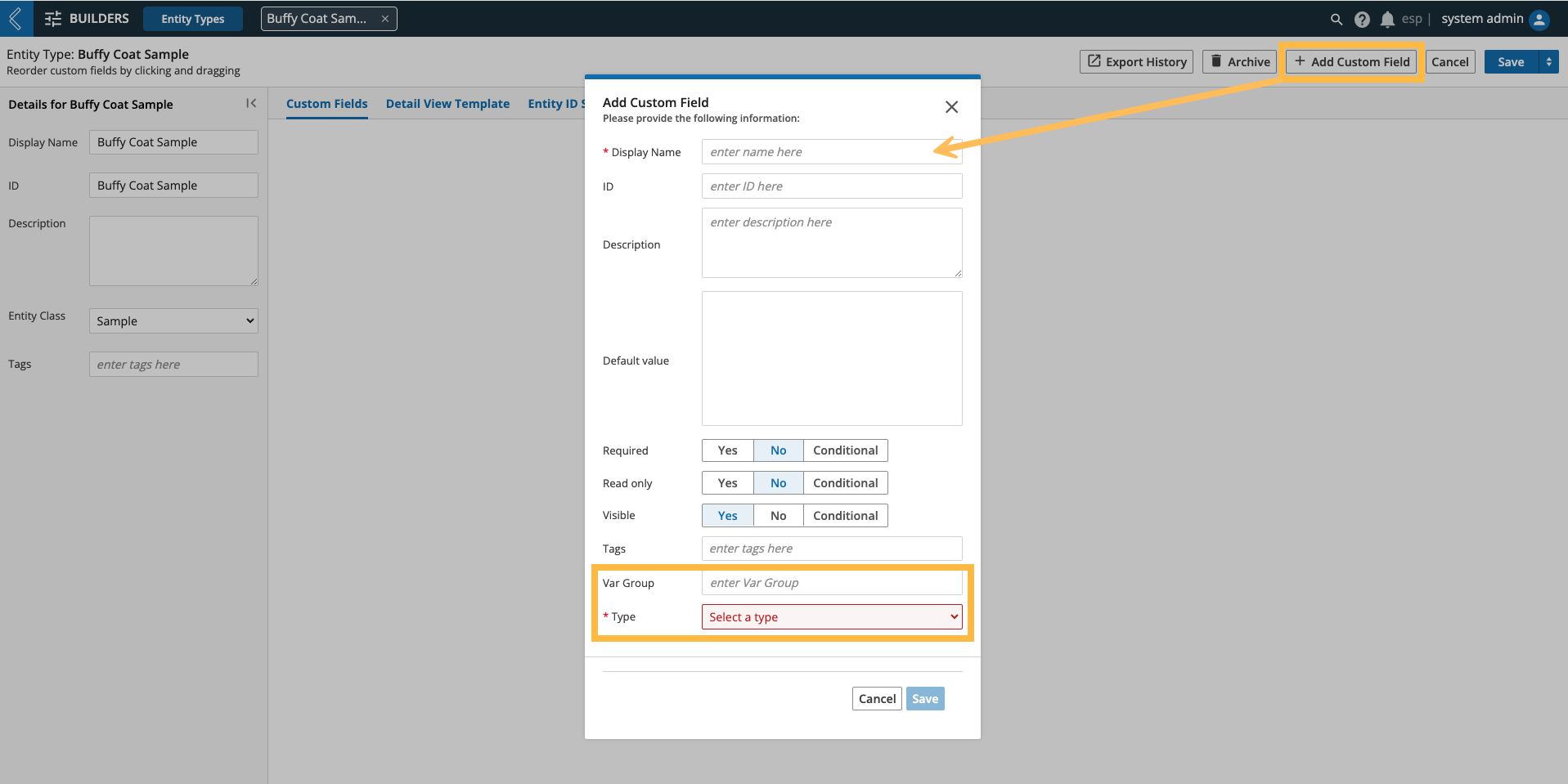 |
Var Group - organizes custom fields into tabs on the Entity details page.
Type - field options include:
Type | Purpose |
Free-form text entry | Enter any character (both text and numbers allowed). |
Numbers only allowed | Enter any number (parameters defined below). |
Picklist | Select one (1) or more options. |
Date/Time | Select a date and/or time in predefined or custom formats. |
Checkbox | Boolean true or false. |
Attachment | Attach a file. |
Barcode | Capture data as a barcode (1D, mini data matrix, or QR). NoteValue does not become the resource’s barcode. |
Resource Link | Link to another L7|ESP resource. If the Link Type is Entity Class, Container, Item, or Service Type, a multi-select picklist will appear to restrict to the selected:
|
Conditionally Required, Read only, Visible
These conditions can only be configured by referencing the value of another custom field associated with the same Entity using the entity_value expression.
Example
For Buffy Coat Samples, Component is a picklist with options Platelets and White Blood Cells. If the latter is selected, another custom field named Target Population should be displayed. This is accomplished by making Target Population conditionally visible using the expression:
{{ entity_value('Component') == 'White Blood Cells' }}
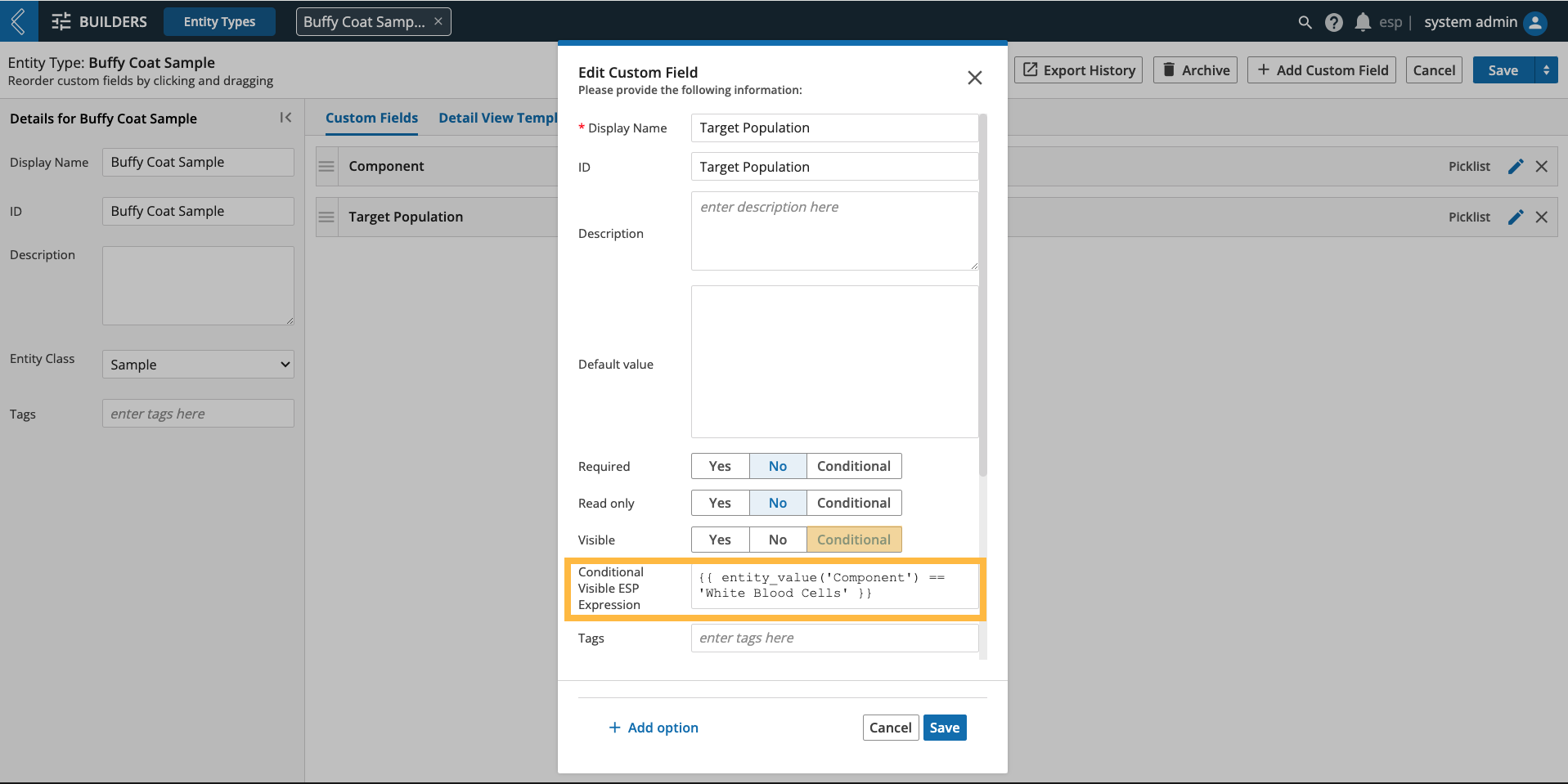 |
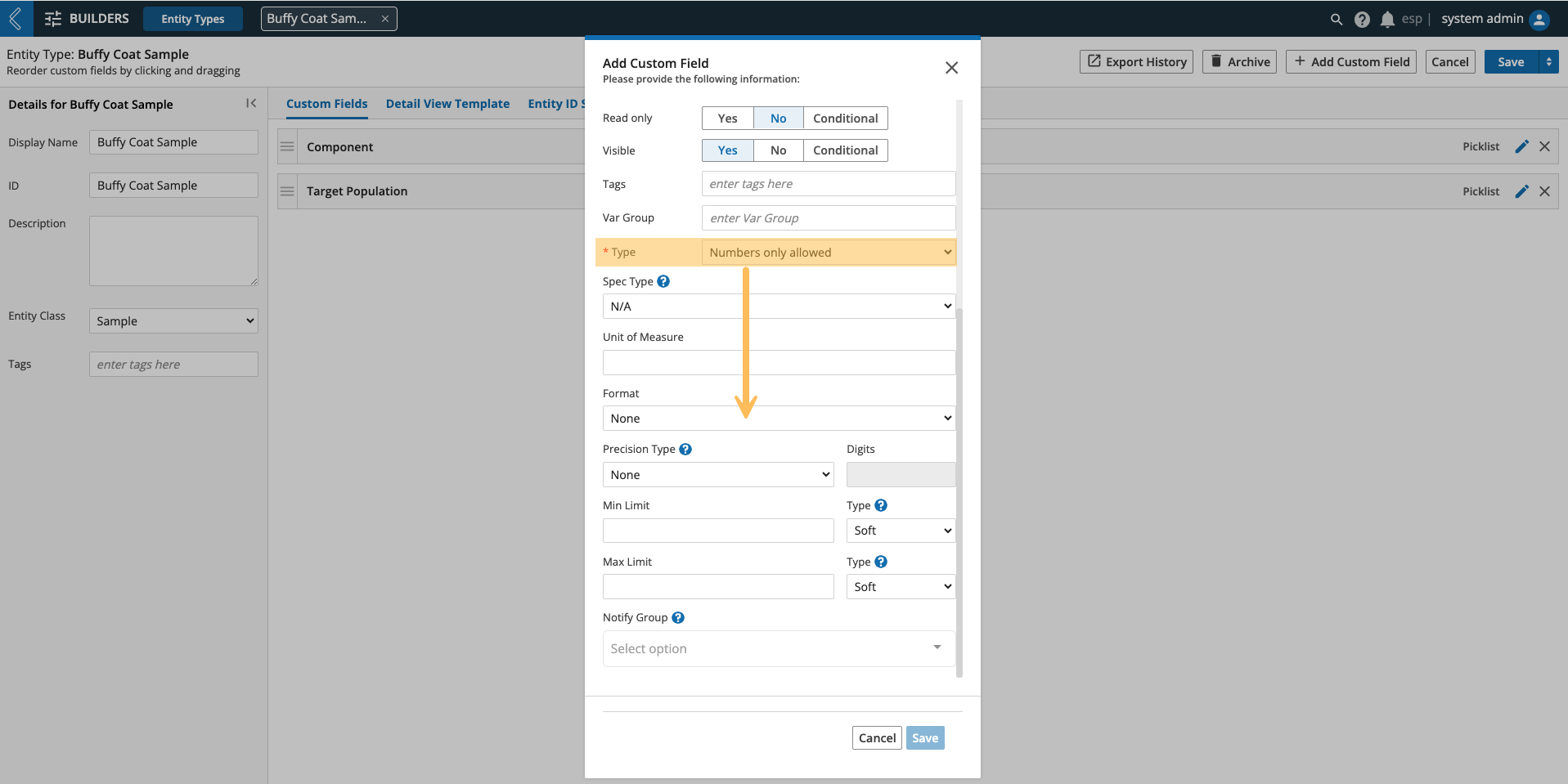
Numeric Fields
Values for numeric fields are not formatted by default, but can be rendered as a percentage or currency.
 |
Note
Percentages should be recorded as decimal values. L7|ESP will automatically convert 0.85 to 85%
Warning
Spec Type and Unit of Measure are not supported in LIMS.
The three-letter currency code dictates precision, whereas percentages and unformatted values can be formatted to a specified number of decimal places or significant figures.
Note
Precision only impacts the displayed value. The underlying value is not changed.
A minimum and maximum limit can be applied to all numeric fields, regardless of format. A row cannot be completed in a LIMS Worksheet if a hard limit is exceeded. In the event a hard limit is exceeded, the field will be colored red and an error message will appear in the bottom-right corner of the screen.
In the event a soft limit is exceeded, the field will be colored orange and the error will be replaced with a warning. These errors and warnings are only visible in LIMS, but can be sent as an L7|ESP notification to one (1) or more Workgroups.
Numeric fields can have the same limits outside of LIMS (i.e., Entities app), but L7|ESP will automatically adjust hard limit excursions to the most recently saved in-range value. This includes null if no in-range value has been saved yet.
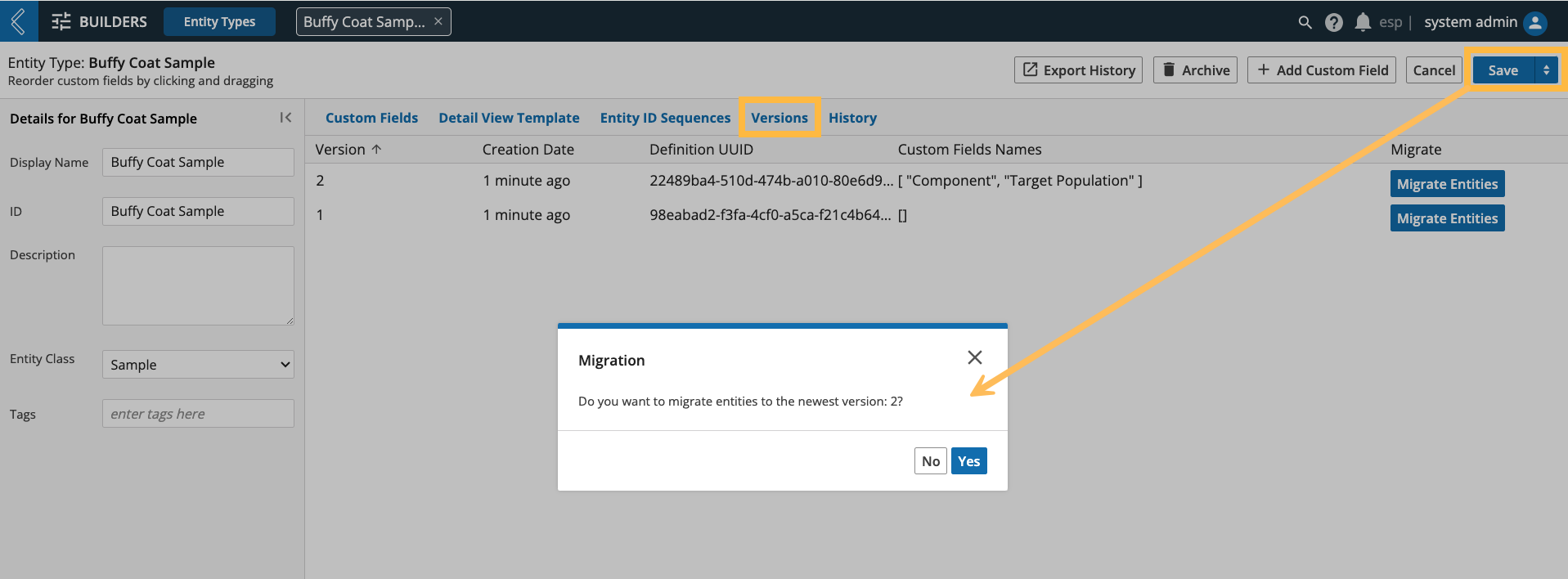
Any changes you make to an Entity Type will be saved as a separate version with the option to migrate existing Entities of the same type to reflect the changes. Otherwise, the saved changes will only apply to newly created Entities.
Warning
Changes to Entity ID Sequences cannot be migrated to existing Entities.
 |